Percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI) has been rapidly evolving since its initial application in 1977. Over the years, it has become a mainstay of the treatment of coronary artery disease, including acute coronary syndromes and stable ischemic heart disease.
With the advent of novel ancillary technologies, such as intravascular ultrasound (IVUS) and optical coherence tomography (OCT), it has become imperative that routine upfront intravascular imaging be incorporated in PCI procedures to improve efficiency and achieve superior clinical outcomes.
As the interventional cardiology community tackles the more complex issues of the coronary artery disease spectrum, and with the introduction of complex and high-risk coronary intervention fellowship programs, the use of intravascular imaging is an important step along the road to a successful PCI procedure.
Systems, such as the Synergy Between Percutaneous Coronary Intervention With Taxus and Cardiac Surgery (SYNTAX) score and the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association lesion classification system, have been developed to characterize and quantify lesion complexity.1,2 Comorbidities, such as congestive heart failure, diabetes, and chronic kidney disease, as well as lesion anatomic factors, such as chronic total occlusion (CTO), bifurcation disease, unprotected left main disease, long lesions, and calcified lesions, have all increased the complexity of the PCI necessary to achieve revascularization.2 Similarly, anatomically complex lesions are associated with lower success rates and higher rates of postprocedural complications when compared with less complex anatomic lesions.2,3 Coronary artery bypass grafting has been shown to be superior to PCI or medical therapy in the case of intermediate–high SYNTAX scores; however, with the advances in PCI technology, interventional cardiologists hope to close that gap and successfully address more complex cases.4 In the past decade, there has already been a twofold increase in the rate of complex PCI, providing better outcomes to more elderly and sicker patients.5 However, considering that there is an inverse relationship between operator volume and in-hospital mortality for PCI patients, there will likely be an additional emphasis on operator experience and high-volume centers for complex PCI.1,6
In the past 30 years, the field of interventional cardiology has witnessed major technological advancements in the field of intravascular imaging. The two modalities of note, IVUS and OCT, are used as adjunctive tools to conventional angiography in order to provide an optimized and precise procedural outcome.
Traditionally, PCI is guided through coronary angiography, which uses a radiopaque contrast dye to visualize the circulation and subsequently quantify any significant intraluminal stenosis. For intermediate complexity lesions, angiography alone may provide sufficient guidance, but coronary angiography has well-known limitations. These include significant intra- and interobserver variability, and limited plaque morphology visualization. IVUS uses a 20–60 MHz frequency ultrasound probe-tipped catheter, particularly useful in situations in which angiography alone provides inadequate visualization. The image created is a 360°, 2D view of the vessel wall. The resolution is around 100 µm axially and 200–250 µm laterally. The image properties are typical of ultrasound-generated images; the image is generated based on the reflection of ultrasound waves, which depend on the physical properties of the vessel components. This technology allows interventionalists to visualize plaque morphology, extent, and composition, as well as stent positioning, stent wall apposition, and stent border characteristics. IVUS can be used before, during, and after the procedure to optimize PCI and improve outcomes.
In clinical use, two types of IVUS systems are available: the solid-state electronic phased array transducer and the mechanical single-element rotating transducer. The 6 Fr compatible mechanical systems offer a more uniform pullback and greater resolution due to the higher ultrasound frequency. Mechanical systems are available commercially as the 60 MHz OptiCross (with or without high definition) catheter (Boston Scientific), the Revolution 45 MHz catheter (Philips), and the 40 MHz LipiScan IVUS (InfraReDx). The solid-state phased array transducer has 64 stationary transducer elements around the tip that image at 20 MHz, and it is commercially available as the 5 Fr-compatible Eagle Eye Catheter (Volcano). Benefits of the solid-state catheter include superior deliverability due to the coaxial design and lack of non-uniform rotational distortion artifacts seen with rotational systems.7
Another novel imaging modality in the armamentarium of interventional cardiologists is OCT. OCT uses near-infrared light (1,300 nm wavelength) to image the lumen–wall interface of coronary arteries. Image generation depends on the time delay of light wave reflection. While OCT has a superior spatial resolution, it has a few important drawbacks. These include a low tissue penetration of around 1–2 mm and the need to create a blood-free zone to properly image the vessel wall. The wavelength of light is smaller than the diameter of a red blood cell, thus a blood-free zone is needed to prevent interference. This is accomplished by crystalloid or contrast flush of the vessel, followed by a constant pullback to acquire the image.8
There are limited trials comparing IVUS and OCT use in guiding lesion-specific complex PCI. Several studies have compared their use in PCI in general. OCT has better reproducibility in measuring lumen parameters, although its relatively lower penetration does not allow optimal vessel size measurement.9,10 This limits the operator to sizing stents based on luminal size rather than vessel size, yielding smaller stent diameters.9,10
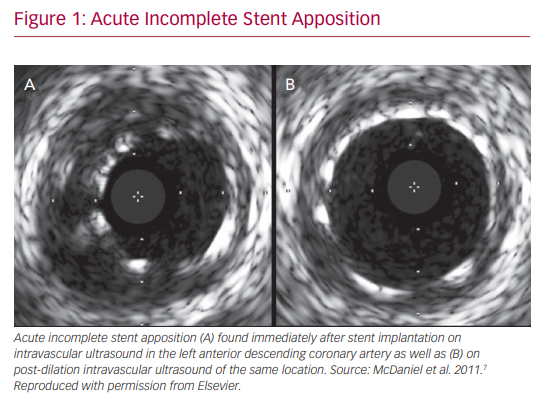
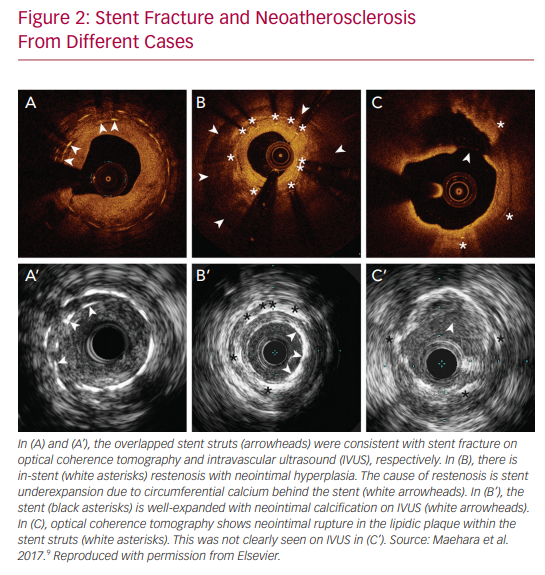
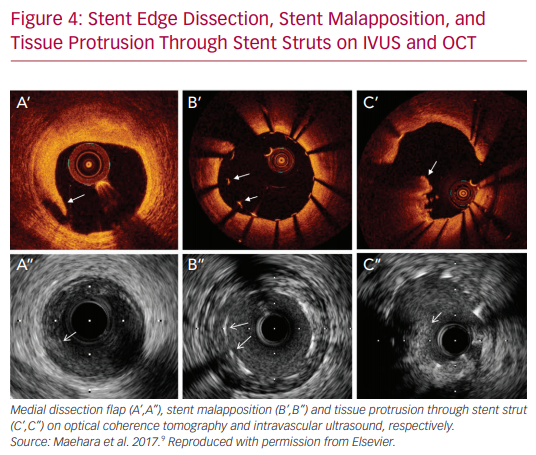
IVUS and OCT are excellent for detecting calcifications, which is important in determining whether atherectomy is necessary prior to stent implantation. However, IVUS cannot visualize fibrocalcific lesions as well as OCT, due to the acoustic shadowing caused by the reflection of ultrasound waves on the calcium.11 The finer resolution provided by OCT is also able to detect smaller stent edge dissections compared with IVUS.12 The Observational Study of Optical Coherence Tomography (OCT) in Patients Undergoing Fractional Flow Reserve and Percutaneous Coronary Intervention – Stage II (ILUMIEN II) trial retrospectively compared OCT-guided and IVUS-guided PCI, and found that OCT detected a higher prevalence of post-PCI stent malapposition, edge dissections, and tissue protrusion (Figures 1–4).12
Although the higher resolution can make up for the low tissue penetration with OCT, one disadvantage of OCT is the higher dose of contrast needed to create a blood-free zone. This amount was determined by the ILUMIEN III study to be around 32 ml additional contrast use, on average.13 This need for clearance limits the ability to image ostial left main lesions and the additional contrast is worrisome for patients with poor renal function.
IVUS plays an important role in many aspects of complex, PCI whether it is preoperative planning, intraoperative positioning, or postoperative assessment. Its use is imperative in a myriad of clinical subsets including CTO, in-stent restenosis, complex coronary bifurcation stenosis, left main PCI, and saphenous vein graft stenoses.
In coronary bifurcation PCI, IVUS has been shown to be useful in determining stenting strategies, stent placement, and has even demonstrated improved long-term clinical outcomes.7 For instance, selection of provisional or complex two-stent bifurcation techniques in the distal left main bifurcation lesions should be based on disease status of the ostium of the left circumflex artery. In this setting, IVUS provides accurate information for both main-branch and side-branch disease patterns and the status of vascular positive or negative remodeling in these lesions.7
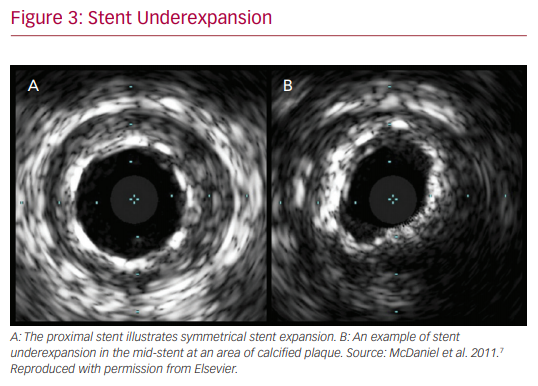
In addition to the assistance in the choice of stenting strategy, IVUS has a role in optimizing stent mechanics intraoperatively. It provides valuable information on stent expansion and adequate apposition. Risk factors for stent thrombosis and restenosis include stent malapposition and underexpansion. IVUS evaluation ensures achievement of larger stent diameters and simultaneously provides information on acute incomplete stent malapposition. IVUS criteria for minimum stent area predicting angiographic restenosis were 5.0 mm2 for the left circumflex artery ostium, 6.3 mm2 for the left anterior descending artery ostium, 7.2 mm2 for the polygon of confluence, and 8.2 mm2 for the proximal left main coronary artery (LMCA) above the polygon of confluence (so-called 5–6–7–8 rule).14 It is noted that the population was Asian, and that left main cut-off values are larger in white patients.
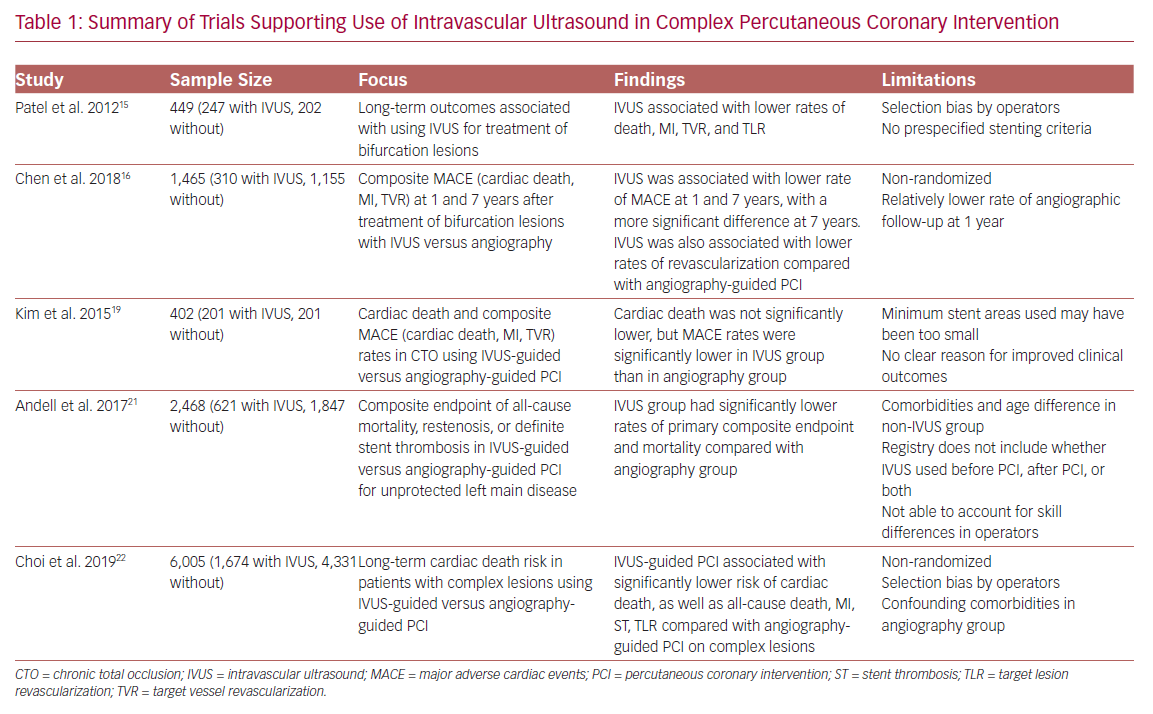
Additionally, Patel et al. found that at 2.5 years after complex PCI, IVUS use was associated with a decreased incidence of death, MI, stent thrombosis, target lesion revascularization (TLR) and target vessel revascularization (TVR).15 Another study found similar results with regard to reduced revascularization, MI, and cardiac death for IVUS-guided drug-eluting stent (DES) implantation in patients with unstable angina and true bifurcation lesions.16
In the CTO subset of lesions, the role of IVUS has yet to be solidified with hard clinical endpoints. Its utility in CTO lesions has been limited to some preprocedural planning and lesion characterization as well as guiding the reverse controlled antegrade and retrograde tracking technique of revascularization.17,18 Although a reduction in major adverse cardiac events was found, one study failed to show a significant reduction in mortality with IVUS-guided versus angiography-guided PCI in CTO.19 This highlights the difficulty of the procedure as well as the further research needing to be done with IVUS use in CTO PCI.
Perhaps the most extensively researched IVUS use in complex PCI would be its application in unprotected LMCA PCI. Due to the large vascular territory subtended by the left main and its association with high mortality rates, coronary artery bypass grafting has been the standard approach to revascularization. However, due to the advent of improved stent engineering and the utilization of intravascular imaging, PCI outcomes have been shown to be favorable in multiple clinical trials involving this subset of patients.
The Evaluation of XIENCE versus Coronary Artery Bypass Surgery for Effectiveness of Left Main Revascularization (EXCEL) trial is one example of the advancement made in left main PCI over the years.20 Numerous other small studies have demonstrated benefits of IVUS, but one of the largest, conducted by Andell et al., found that IVUS-guided PCI in unprotected LMCA was associated with significantly lower occurrence of all-cause mortality, restenosis, and definite stent thrombosis compared with unprotected LMCA PCI without IVUS guidance.21 The IVUS patients in that study had significantly larger stent diameters, which were independently associated with improved outcome.22 It is hypothesized that stent underexpansion may contribute to stent thrombosis or in-stent restenosis, thus emphasizing the importance of the increased stent diameters achieved with the use of IVUS.
Additionally, a recent meta-analysis found significant reduction in major adverse cardiac events, TLR, and TVR in IVUS-guided DES implantation compared with angiography-guided implantation in patients with complex coronary lesions.22 That study used a broad and appropriate definition of complex lesions, and used cardiac death during 64 months of median follow-up as its primary endpoint. The greatest benefits were seen in the left main group. Lending credence to the aforementioned literature, the role of IVUS in LMCA PCI is essential and a cornerstone of the revascularization process. More randomized clinical trials involving LMCA revascularization need to incorporate the use of intravascular imaging for a true measure of clinical benefit.
Finally, the incremental benefit of IVUS in the PCI realm was noted to have different etiologies in the bare-metal stent (EMS) versus DES categories. In the former, it is noted that IVUS leads to decreased TVR by virtue of decreasing restenosis and increasing minimum stent areas on imaging. As mentioned, stent underexpansion is a major risk factor in the development of restenosis, ultimately leading to TVR.
One meta-analysis of 2,193 patients from seven randomized trials, in which an IVUS-guided PCI strategy was utilized with EMS, found a reduction in TVR (13% versus 18%, p<0.001) in the IVUS-guided subgroup compared with the angiography-guided PCI strategy, with similar rates of death (2.4% versus 1.6%, p=0.18) and MI (3.6% versus 4.4%, p=0.51).23 As mentioned above, clinically significant benefits in death or MI have not been demonstrated in these trials.
In contrast, IVUS guidance in the early DES era has not been shown to influence the rates of restenosis. The contemporary literature, however, indicates reduced TVR with DES and IVUS specifically in the complex lesion subset (Table 1). Larger IVUS MSA cut-offs were also associated with non-ischemic fractional flow reserve.24–27
Additionally, there is mounting evidence that IVUS may reduce the rates of stent thrombosis. Also, an IVUS-guided approach was associated with reduced rates of stent thrombosis at both 30 days (0.5% versus 1.4%, p=0.046) and at 12 months (0.7% versus 2.0%, p=0.014) when compared with an angiography-guided strategy in a propensity-matched analysis of 884 patients undergoing PCI with DES.2,4 The proposed hypothesis behind this benefit is that IVUS aids in the detection of many of the risk factors of stent thrombosis including edge dissections, stent underexpansion, incomplete stent apposition, incomplete lesion coverage, geographic miss, residual thrombus and tissue protrusion.28,29
Conclusion
While there are limited studies on the use of IVUS versus OCT in complex PCI, the benefit of IVUS-guided PCI over conventional angiographically guided PCI has been well-delineated in the literature involving multiple clinical subsets including the complex PCI population. It is imperative that routine upfront utilization of intravascular imaging be used in complex PCI procedures, including the left main subset, due to the overwhelming evidence for and benefits of superior clinical outcomes and lower incidences of restenosis and stent thrombosis. Conventional angiography alone cannot ensure proper stent expansion and apposition needed for the superior outcomes and reduced complications provided by IVUS-guided PCI.29
Finally, we await the results of the upcoming IMPact on Revascularization Outcomes of intraVascular Ultrasound Guided Treatment of Complex Lesions and Economic Impact (IMPROVE; NCT04221815) randomized controlled trial that is specifically assessing the impact of IVUS in PCI of complex coronary stenoses in an estimated sample size of 3,100 patients.30